
|
An Open Source, Royalty-free, Real-time Operating System |
What is Prex?
Prex is an open source, royalty-free, real-time operating system for embedded systems. It is designed and implemented for resource-constrained systems that require predictable timing behavior. The highly portable code of Prex is written in 100% ANSI C based on traditional microkernel architecture.
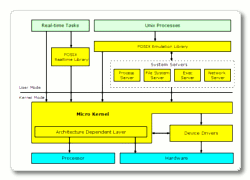 The Prex microkernel provides only fundamental features for task, thread,
memory, IPC, exception, and synchronization.
The other basic OS functions - process, file system, application
loading, and networking, are provided by the user mode servers.
In addition, Prex provides a POSIX emulation layer
in order to utilize existing *NIX applications.
This design allows the system
to perform both of the native real-time task and the generic POSIX process
simultaneously without degrading real-time performance.
It also helps platform designers to construct OS
by choosing suitable system servers for their target requisition.
The Prex microkernel provides only fundamental features for task, thread,
memory, IPC, exception, and synchronization.
The other basic OS functions - process, file system, application
loading, and networking, are provided by the user mode servers.
In addition, Prex provides a POSIX emulation layer
in order to utilize existing *NIX applications.
This design allows the system
to perform both of the native real-time task and the generic POSIX process
simultaneously without degrading real-time performance.
It also helps platform designers to construct OS
by choosing suitable system servers for their target requisition.
Project Goals
The project targets the following goals:- To provide a small, portable, real-time, secure, and robust operating system.
- To provide simple and clean source codes for education and an experimental test-bed.
- To conform to open standards as much as possible.
- To enjoy our life with kernel hacking. ;-)

License
Prex is royalty-free software released under Revised BSD License.
Features
Prex has the following features:- Task & Thread Control: preemptive priority scheduling with 256 priority levels
- Memory Management: memory protection, virtual address mapping, shared memory, MMU or MMU-less configuration
- IPC: object name space, synchronous message passing between threads
- Exception: fault trapping, framework for POSIX signal emulation
- Synchronization: semaphores, condition variables, and mutexes with priority inheritance
- Timers: sleep timers, one-shot or periodic timers
- Interrupt: nested interrupt service routines, and prioritized interrupt service threads
- Device I/O: minimum synchronous I/O interface, DPC (Deferred Procedure Call)
- Security: task capability, pathname-based access control, I/O access permission.
- Real-time: low interrupt latency, high resolution timers and scheduling priority control
- Power Management: power policy, idle thread, DVS (Dynamic Voltage Scaling)
- Debugging Facility: event logging, kernel dump, GDB remote debug
- File Systems: multi-threaded, VFS framework, buffer cache, ramfs, fatfs, arfs, etc.
- POSIX Emulation: pid, fork, exec, file I/O, signal, pipe, tty, pthread, etc.
- Libc: C library fully optimized to generate a small executable file
- CmdBox: a small binary that includes tiny versions of many UNIX utilities.
- Networking: (plan) TCP/IP stack, BSD socket interface
Hardware Requirements
 Prex minimum hardware requirements are as follows:
Prex minimum hardware requirements are as follows:
- Processor: 32-bit Processor (x86, ARM, PowerPC)
- Memory: 256KB of RAM (Kernel < 25k bytes)
- Timer: programmable interval timer
Note: RAM requirements may vary depending on the number of system servers being supported.
Copyright© 2005-2009 Kohsuke Ohtani

